How to connect multiple PTZ cameras to controller
Discover how to connect multiple Pan-Tilt-Zoom (PTZ) cameras to a single controller in this blog post. Whether you’re a professional videographer, a streaming enthusiast, or setting up a surveillance system, this comprehensive guide will walk you through the two main types of PTZ joystick controllers: software-based and hardware-based, ensuring you make the best choice for your needs.
Types of PTZ Joystick Controllers
There are two different categories of PTZ joystick controllers that support multiple cameras. The first category of PTZ controllers are software based. Software based controllers almost exclusively use IP connectivity to control PTZ cameras although there are UVC (the ability to control USB cameras) and serial (the ability to convert Serial to USB) control options as well. Software PTZ camera controllers include the PTZOptics Camera Management Platform (CMP), and popular software such as OBS and vMix.
Software-Based PTZ Joystick Controllers
In the dynamic world of PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) camera control, software-based joystick controllers emerge as a forefront solution, offering versatility and convenience for users. These controllers are particularly favored in setups where flexibility and integration with various systems are crucial. In this section, we will explore the key features, benefits, and popular examples of software-based PTZ controllers.
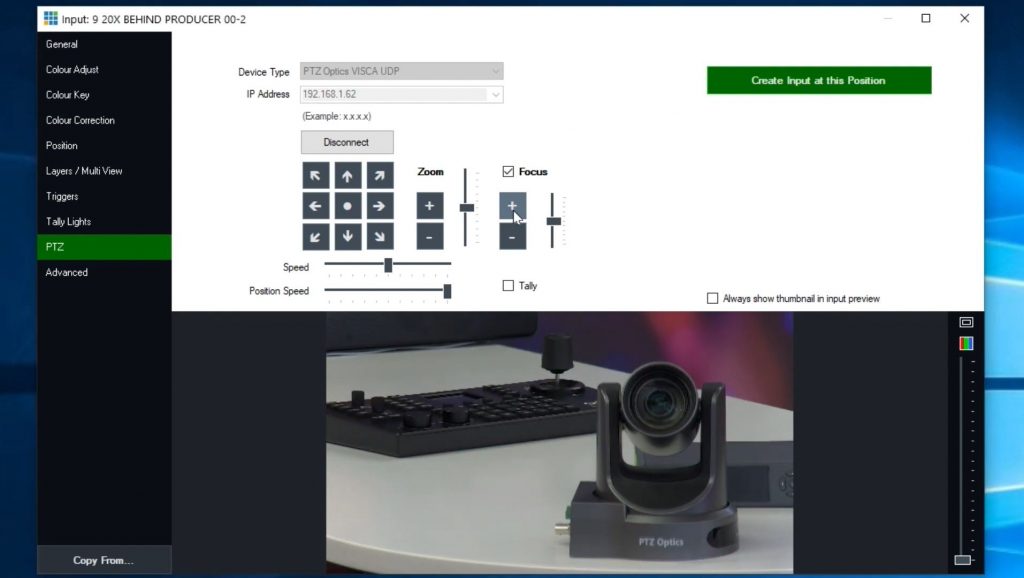
Key Features and Benefits
Software-based PTZ controllers are distinguished by their reliance on IP (Internet Protocol) connectivity. This feature allows for seamless integration with networked camera systems, offering a level of convenience and control that is unmatched by traditional methods. Here are some of the standout features and benefits:
- Ease of Integration: These controllers effortlessly connect with IP-enabled PTZ cameras, making them an ideal choice for modern, networked environments.
- UVC Compatibility: For added versatility, many software-based controllers support UVC (USB Video Class), enabling control over USB-connected cameras. This feature expands the range of cameras that can be managed through the software.
- Serial-to-USB Conversion: Addressing the need for legacy system integration, these controllers often include options for Serial-to-USB conversion, ensuring compatibility with a wider array of camera systems.
Popular Software-Based Controllers
To give you a clearer picture of what’s available in the market, let’s look at some of the most popular software-based PTZ camera controllers:
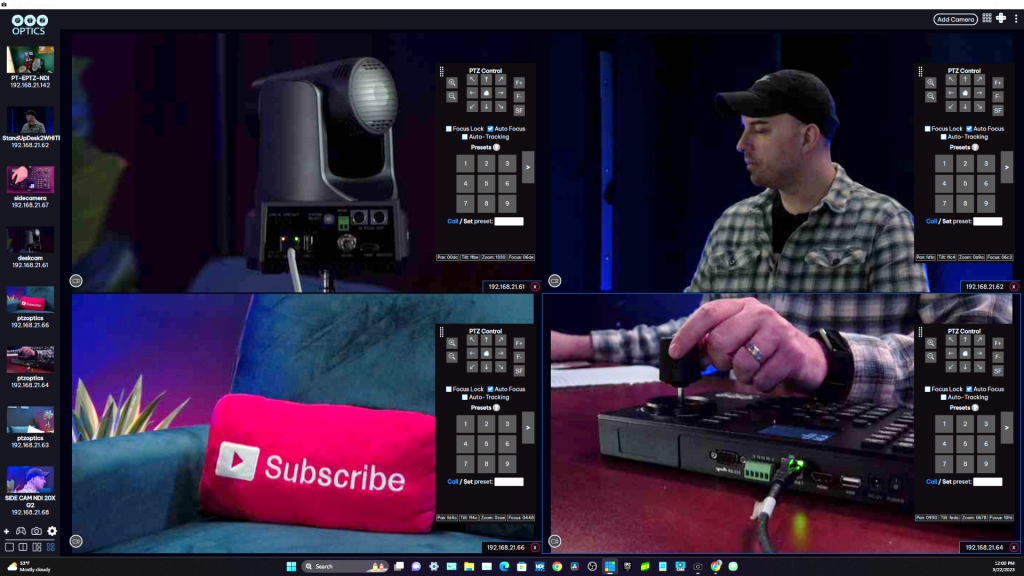
- PTZOptics Camera Management Platform (CMP): This platform stands out for its user-friendly interface and robust functionality, making it a top choice for both beginners and professionals. It’s designed to provide comprehensive control over PTZOptics cameras, along with a host of customization options.
- OBS (Open Broadcaster Software): Widely known in the streaming community, OBS is not just a broadcasting tool but also a capable PTZ camera controller. Its open-source nature allows for extensive customization and integration with a variety of camera models.
- vMix: A powerhouse in live production software, vMix offers integrated PTZ camera control, catering to users who require a combination of video mixing, switching, and live streaming capabilities alongside camera management.
Setting Up and Using Software-Based Controllers
Setting up a software-based PTZ controller is generally straightforward. The process typically involves installing the software on a compatible device, connecting the PTZ cameras to the same network, and configuring the cameras within the software interface. Users can enjoy real-time control over camera movements, presets, and other settings directly from their computer or mobile device.
Hardware-Based PTZ Joystick Controllers
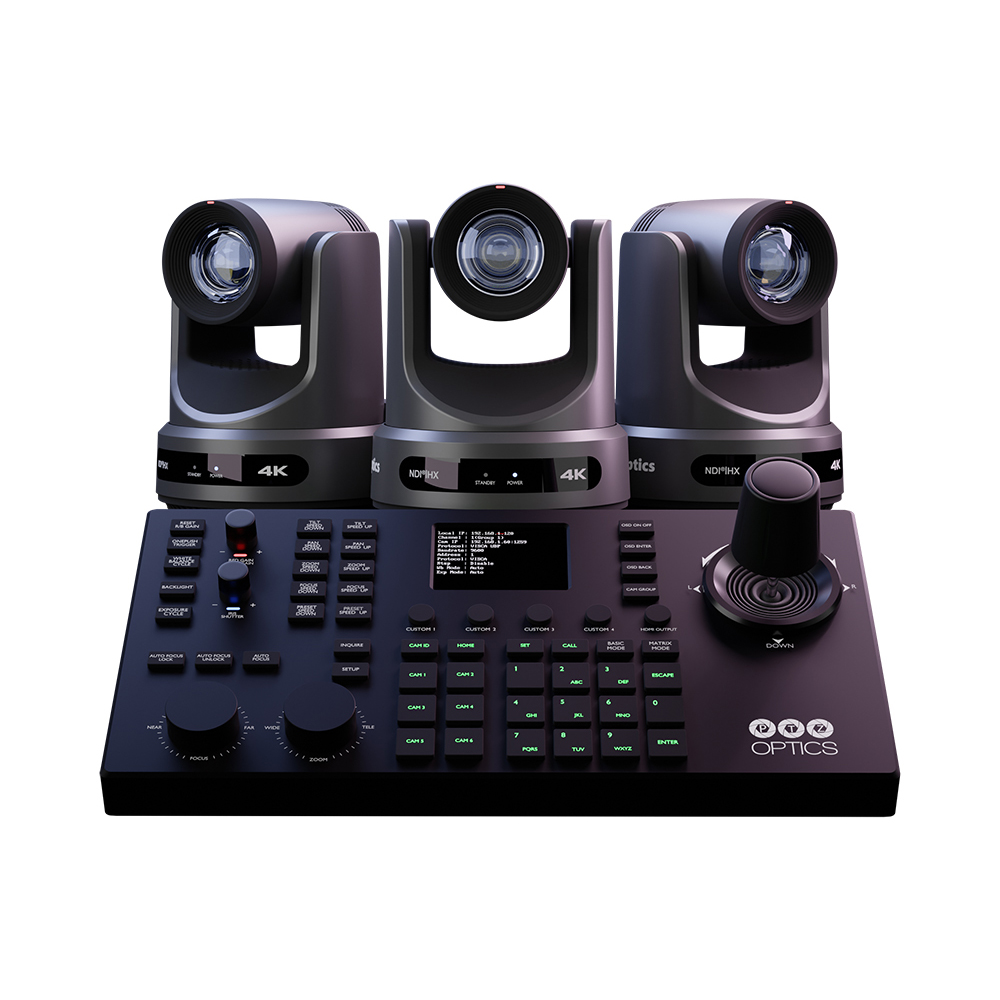
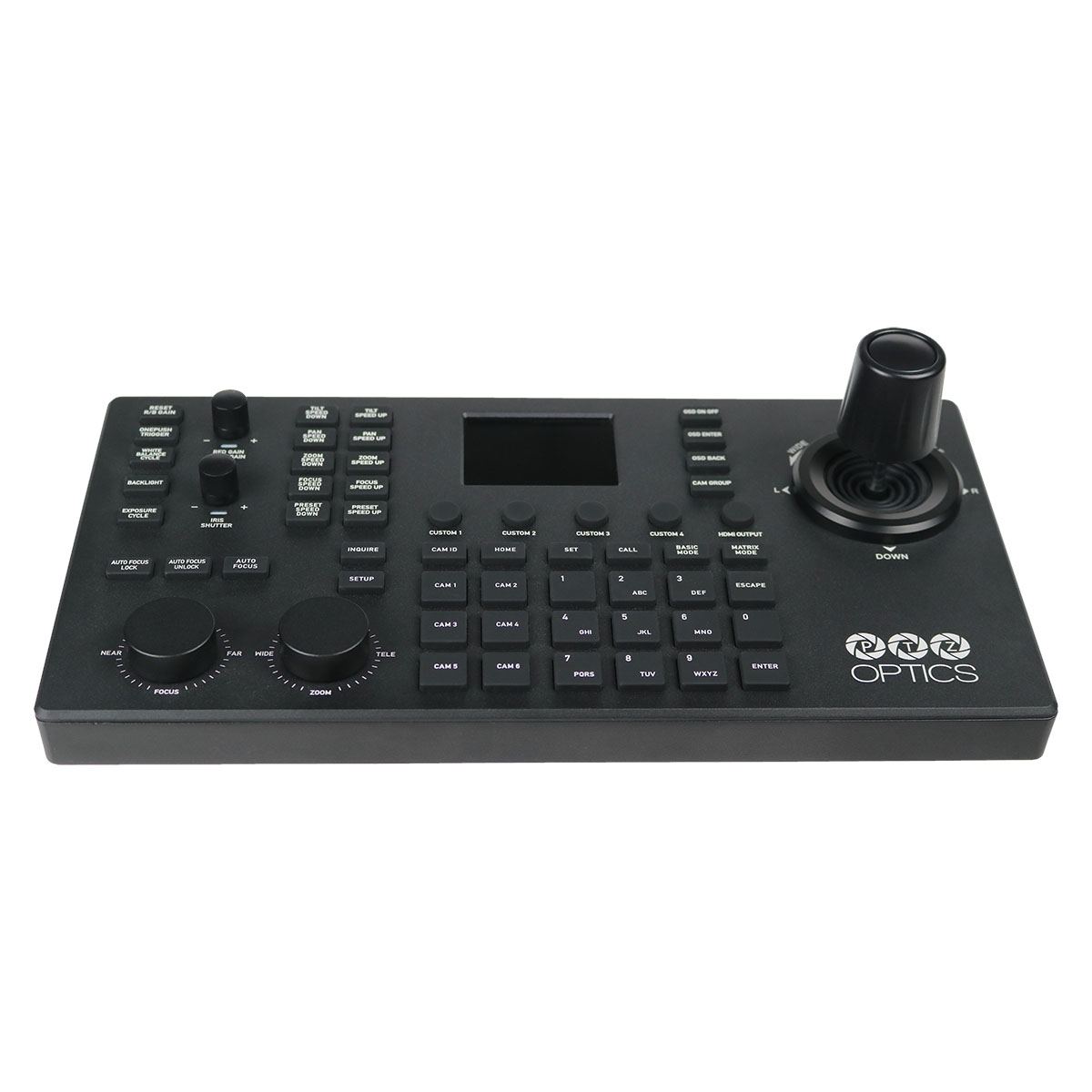
The second category of PTZ camera controllers are hardware joysticks. Hardware-based PTZ joystick controllers come in two main types: Serial and network based. Some PTZ joystick controllers such as the PTZOptics SuperJoy and PT-JOY-G4 support both Serial and Network control options. For demonstration purposes, we will use the HuddleCamHD HC-JOY-G4 joystick controller, for serial connected cameras and the PTZOptics SuperJoy to demonstrate IP connected cameras.
Tip: Learn more about networking for managing IP-connected cameras here.
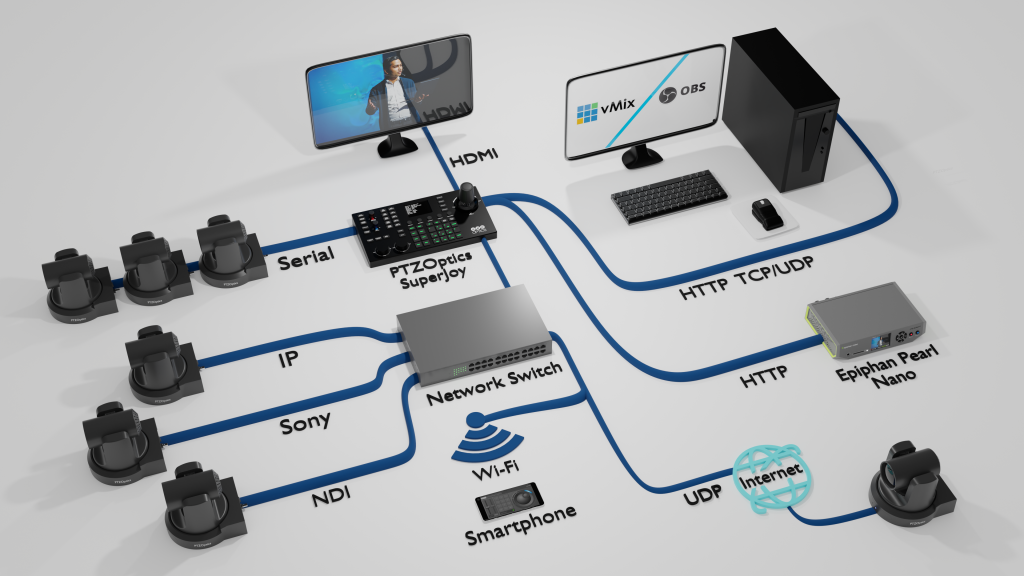
Transitioning from the digital realm of software, we enter the tangible world of hardware-based PTZ joystick controllers. These controllers provide a tactile, hands-on approach to camera control, favored in many professional settings for their precision and reliability. This section will cover the types, features, and some notable examples of hardware-based joystick controllers.
Types of Hardware-Based Controllers
Hardware joystick controllers for PTZ cameras generally fall into two categories, each catering to different connectivity and control needs:
- Serial Controllers: These controllers use direct, physical connections to control cameras. They are known for their reliability and are often preferred in setups where wireless connectivity might be unstable.
- Network-Based Controllers: These devices control cameras over a network connection. They are versatile and can control multiple cameras across different locations, provided they are on the same network.
Key Features of Hardware Controllers
Hardware-based controllers are designed with the following key features:
- Physical Joystick and Buttons: Offering a tactile experience, these controllers allow for precise adjustments and quick access to functions through physical controls.
- Dual Control Options: Some models, like the PTZOptics SuperJoy and PT-JOY-G4, offer both Serial and Network control options, providing versatility in various environments.
- Durable Build: Often built to withstand the rigors of professional use, these controllers boast a sturdy construction, ensuring longevity and reliability.

Popular Hardware-Based Controllers
Let’s take a closer look at some popular hardware-based PTZ joystick controllers:
- PTZOptics SuperJoy: A versatile controller, the SuperJoy is known for its ability to manage both serial and IP-connected cameras. It’s user-friendly and packed with features that cater to both beginners and seasoned professionals.
- HuddleCamHD HC-JOY-G4: Ideal for serial-connected camera setups, this controller is praised for its intuitive design and ease of use, making it a favorite for those who prefer a straightforward, efficient control system.
- PT-JOY-G4: Another versatile option, this controller supports both Serial and Network connections, allowing for seamless control of a diverse range of camera setups.
Practical Demonstration with Controllers
To illustrate the use of these controllers, the video above demonstrates:
- Using the HuddleCamHD HC-JOY-G4 for controlling serial-connected cameras.
- Employing the PTZOptics SuperJoy for managing IP-connected cameras.
This hands-on demonstration will provide insights into the setup process, connection methods, and operational nuances of these controllers.
Hardware-based PTZ joystick controllers offer a reliable and intuitive way to manage PTZ cameras. They are particularly useful in environments where direct control and precision are paramount. With options for both serial and network connections, these controllers ensure that users can find the perfect fit for their specific camera control needs. Next, we will explore the various methods of controlling PTZ cameras, delving into the specifics of IR remote control, IP, and serial connections.
Overview of PTZ Camera Control Methods
PTZ cameras offer a range of control options to suit different requirements and setups. Understanding these methods is crucial for efficient operation and optimal camera use. This section focuses on the various ways PTZ cameras can be controlled, including Infrared (IR) remote control, IP connections, and serial connections.
Infrared (IR) Remote Control
IR remote control is the most straightforward method for managing PTZ cameras. It’s suitable for smaller setups or situations where simple point-and-click control is sufficient. Key points include:
- Ease of Use: IR remotes offer a familiar and easy-to-understand interface.
- Direct Line of Sight: They require a direct line of sight to the camera, limiting their range and flexibility.
- Basic Functionality: IR remotes typically provide basic functions like pan, tilt, zoom, and preset recall.

IP Connections
Controlling PTZ cameras over IP networks provides flexibility and scalability. This method is ideal for larger setups or when remote control is necessary. Aspects to consider are:
- Network Configuration: Cameras and controllers must be on the same network. This setup allows for remote control from different locations.
- Advanced Features: IP control often comes with more sophisticated features like camera grouping, advanced preset configurations, and software integration.
- Security and Reliability: Ensure network security to prevent unauthorized access, and a stable network connection is crucial for uninterrupted control.
Serial Connections
Serial control, involving physical connections between the controller and cameras, offers reliability and precision, especially in environments where wireless connectivity might be problematic. Key elements include:
- Daisy-Chaining Cameras: Serial connections often use a daisy-chain configuration. This involves connecting the first camera to the controller and then linking each subsequent camera in sequence.
- Cable Types and Connections: Typically, a DB9 serial cable connects the hardware joystick controller to the first PTZ camera using a DB9 to 8-pin mini-din connection. From the first camera to the next, an 8-pin mini-din cascade cable is used.
- Assigning Serial IDs: Each camera in the daisy-chain should have a unique serial ID, set through the camera’s On Screen Display (OSD) menu. This ID ensures the controller commands the correct camera.
The method chosen for controlling PTZ cameras depends on various factors like the size of the setup, the level of control required, and the specific environment. IR remote control offers simplicity, IP connections provide flexibility and advanced features, while serial connections deliver reliability and precision. Understanding these methods allows users to tailor their control setup to their specific needs and preferences. In the following section, we will delve deeper into setting up IP joystick controllers, a crucial aspect of managing network-connected PTZ cameras.
Setting Up IP Joystick Controllers for PTZ Cameras
In the diverse landscape of PTZ camera control, IP joystick controllers stand out for their ability to manage multiple cameras over a network. This section offers a detailed guide on setting up and using IP joystick controllers, ensuring a seamless integration of PTZ cameras into your network for efficient control and monitoring.
Essentials of IP Joystick Controller Setup
Setting up an IP joystick controller involves several key steps to ensure that each camera is correctly connected and responsive to the controller’s commands. Here’s what you need to know:
1. Assigning Static IP Addresses to Cameras
- Importance of Static IPs: Assigning static IP addresses to each PTZ camera is crucial for a stable connection. Static IPs prevent address changes, which can disrupt the control link between the camera and the controller.
- How to Assign: This can typically be done through the camera’s web interface or on-screen display settings. Ensure each camera has a unique IP address within the network’s range.
2. Configuring the IP Joystick Controller
- Accessing the Controller Interface: Most IP joystick controllers have a unique IP address or web interface. This allows you to log into the controller for configuration.
- Entering Camera IPs: Once logged in, you’ll input the static IP addresses of your PTZ cameras. This step is crucial to establish a connection between the controller and the cameras.
Adding Cameras to the Controller
- Using the Web Interface: Enter each camera’s IP address along with a corresponding camera ID in the controller’s web interface. This ID is used to select and control individual cameras from the joystick.
- Direct Addition from the Joystick: Many controllers also allow you to add and configure cameras directly from the joystick interface, providing an alternative for users who prefer hands-on setup.
Best Practices for IP Joystick Controller Setup
- Network Considerations: Ensure your network is capable of handling the data traffic from multiple PTZ cameras. This might involve network upgrades or adjustments.
- Firmware Updates: Keep both your cameras and joystick controller firmware up to date to ensure compatibility and access to the latest features and security updates.
- Regular Testing and Maintenance: Regularly test the setup to ensure all cameras are responsive and the control links are stable. Routine maintenance helps in early identification of potential issues.
IP joystick controllers offer a powerful and flexible way to manage multiple PTZ cameras over a network. By carefully setting up and configuring these controllers, you can achieve efficient, centralized control of your camera system, ideal for applications like live streaming, broadcasting, surveillance, and more. With the insights provided in this guide, you’re now equipped to optimize your PTZ camera control setup for maximum efficiency and ease of use.
Summary and Final Thoughts on Connecting Multiple PTZ Cameras
In this comprehensive guide, we have explored the diverse world of PTZ (Pan-Tilt-Zoom) camera control, focusing on the two primary categories of controllers – software-based and hardware-based – and the various methods to control PTZ cameras. Let’s briefly recap the main points:
- Software-Based Controllers: These controllers, such as the PTZOptics Camera Management Platform, OBS, and vMix, offer flexibility with IP connectivity and options for UVC and serial-to-USB conversions.
- Hardware-Based Controllers: With physical joysticks and buttons, controllers like the PTZOptics SuperJoy and HuddleCamHD HC-JOY-G4 provide tactile feedback and precision, supporting both serial and network connections.
- Controlling Methods: We discussed IR remote control, IP connections, and serial connections, each offering unique benefits from simplicity to advanced network control.
- Setting Up IP Joystick Controllers: This involves assigning static IP addresses to cameras, configuring the joystick controller, and adding cameras to the controller for efficient network-based control.
Final Thoughts and Recommendations
Choosing the right controller and control method is crucial for an efficient PTZ camera setup. Here are some final recommendations:
- Assess Your Needs: Consider the size and complexity of your setup, and choose a controller that meets these requirements.
- Invest in Quality: Opt for controllers known for their reliability and user-friendliness.
- Stay Updated: Regularly update your software or firmware to keep your system running smoothly.
- Plan for Expansion: If you anticipate expanding your camera setup, choose a controller that can accommodate more cameras and offers scalability.
- Seek Support When Needed: Don’t hesitate to contact customer support or refer to online resources for help during setup or troubleshooting.
Encouraging Community Engagement
We invite you to share your experiences or ask questions in the comments below. Whether you’re a seasoned professional or new to PTZ cameras, your insights and queries enrich our community’s knowledge and understanding.
Conclusion
Connecting multiple PTZ cameras to a controller can be a straightforward process with the right knowledge and tools. By understanding the different types of controllers and control methods available, you can create a setup that not only meets your current needs but is also prepared for future advancements. Happy filming, streaming, or surveilling!